Hydrogen Helium Table
- Hydrogen Helium Periodic Table
- Hydrogen Helium Lithium Table
- Hydrogen Vs Helium
- Helium Vs Hydrogen Balloon
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Helium - He
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of Helium - He :
(values at 25oC (77oF, 298 K) and atmospheric pressure)

| Molecular Weight | 4.0026 |
| Specific Gravity, air = 1 | 0.138 |
| Specific Volume (ft3/lb, m3/kg) | 97.86, 6.11 |
| Density of liquid at atmospheric pressure (lb/ft3, kg/m3) | 7.80, 125 |
| Absolute Viscosity (lbm/ft s, centipoises) | 13.4 10-6, 0.02 |
| Sound velocity in gas (m/s) | 1015 |
| Specific Heat - cp - (Btu/lboF or cal/goC, J/kgK) | 1.24, 5188 |
| Specific Heat Ratio - cp/cv | 1.66 |
| Gas constant - R - (ft lb/lboR, J/kgoC) | 386, 2077 |
| Thermal Conductivity (Btu/hr ft oF, W/moC) | 0.086, 0.149 |
| Boiling Point - saturation pressure 14.7 psia and 760 mm Hg - (oF, oK) | -452, 4.22 |
| Latent Heat of Evaporation at boiling point (Btu/lb, J/kg) | 10.0, 23300 |
| Critical Temperature (oF, oK) | -450.3, 5.2 |
| Critical Pressure (psia, MN/m2) | 33.22, - |
| Critical Volume (ft3/lb, m3/kg) | 0.231, 0.0144 |
| Flammable | no |
Follow the links below to get values for the listed properties of helium at varying pressure and temperature:
See also more about atmospheric pressure, and STP - Standard Temperature and Pressure & NTP - Normal Temperature and Pressure,
as well as Thermophysical properties of: Acetone, Acetylene, Air, Ammonia, Argon, Benzene, Butane, Carbon dioxide, Carbon monoxide, Ethane, Ethanol, Ethylene, Hydrogen, Hydrogen sulfide, Methane, Methanol, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Pentane, Propane, Toluene, Water and Heavy water, D2O.
Related Topics
590 Oxygen Nitrogen or helium 350 Propane. Nitrogen or helium 660 Sulfur Dioxide Air or nitrogen 590 Sulfur Hexafluoride Argon, helium or Nitrogen 350 Sulfur Hexafluoride Hydrogen 350 Tritium Argon, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, methane, neon, nitrogen, krypton, or xenon CGA Selection Charts Reference Tables Pure Gases CGA Selection Chart for Fittings. Gas Facts includes charts and tables and interactive conversion formulas related to the chemical and physical properties of our cryogenic liquid and compressed gas products, as well as an online tool for estimating the cost of using nitrogen, oxygen, or argon. The first element in the periodic table with more than one electron is helium, which has two electrons. Dot-density diagrams for both these electrons are shown below. One electron is color coded in blue, and the other in green. Note that both electrons occupy the same orbital, namely, a 1s orbital. It turns out that 2 is the maximum. The values in Table 2 were calculated using Henry’s law. For example the concentration of hydrogen gas (H 2) using Henry’s law was obtained by dividing P (which in this case is 1 atm) by K H to get the concentration (C). Table 1 shows that the K H for hydrogen gas is 1282.05.
- Material Properties - Material properties for gases, fluids and solids - densities, specific heats, viscosities and more
Related Documents
- Acetone - Thermophysical Properties - Chemical, physical and thermal properties of acetone, also called 2-propanone, dimethyl ketone and pyroacetic acid. Phase diagram included.
- Air - Thermophysical Properties - Thermal properties of air - density, viscosity, critical temperature and pressure, triple point, enthalpi and entropi, thermal conductivity and diffusicity, and more
- Benzene - Thermophysical properties - Chemical, physical and thermal properties of benzene, also called benzol. Phase diagram included.
- Carbon Dioxide Properties - Properties of saturated liquid Carbon Dioxide - CO2 - density, specific heat, kinematic viscosity, thermal conductivity and Prandtl number
- Critical Points for some Substances - Critical points of some common substances like air, argon, helium and more
- Critical Temperatures and Pressures for some Common Substances - Critical temperatures and pressures for some common substances - air, alcohol, ether, oxygen and more
- Cryogenic Fluids - or Liquefied Gas Properties - Cryogenic properties as density, boiling points and heat of evaporation for fluids like hydrogen, methane, oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine and helium
- Ethane - Thermophysical Properties - Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Ethane - C2H6
- Ethylene - Thermophysical Properties - Chemical, physical and thermal properties of ethylene, also called ethene, acetene and olefiant gas. Phase diagram included.
- Gas Mixture Properties - Special care must be taken for gas mixtures when using the ideal gas law, calculating the mass, the individual gas constant or the density
- Gases - Densities - Densities and molecular weights of some common gases - acetylene, air, methane, nitrogen, oxygen and others ..
- Helium - Density and Specific Weight - Online calculator, figures and tables showing density and specific weight of helium, He, at varying temperature and pressure - Imperial and SI Units
- Hydrogen - Thermophysical Properties - Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Hydrogen - H2
- Ideal Gas Law - The relations between volume, pressure, temperature and quantity of a gas, including definition of density of a gas
- Moist Air Properties - Psychrometric table with humid air properties
- Nitrogen - Enthalpy, Internal Energy and Entropy - Enthalpy, internal energy and entropy of Nitrogen as ideal gas
- Non-ideal gas - Van der Waal's Equation and Constants - Listing of van der Waals constants for more than 200 gases, used to correct for non-ideal behavior of gases caused by intermolecular forces and the volume occupied by the gas particles
- Oxygen - Enthalpy, Internal Energy and Entropy - Enthalpy, internal energy and entropy of oxygen as ideal gas
- Pentane - Thermophysical Properties - Chemical, physical and thermal properties of pentane, also called n-pentane. Phase diagram included.
- Solubility of Gases in Water - Solubility of Ammonia, Argon, Carbon Dioxide, Carbon Monoxide, Chlorine, Ethane, Ethylene, Helium, Hydrogen, Hydrogen Sulfide, Methane, Nitrogen, Oxygen and Sulfur Dioxide in water
Here are a collection of mnemonic sentences supplied by Neville Holmes (6/00) of Australia for the elements in the first four periods of the chemical Periodic Table.
Period 1-2 (Elements 1-10):
Happy Henry Lithely Began Baking Cakes, Not Omitting Four Necessities
Period 2-3: (Elements 11-18):
Naval Magistrates Always Signal Per Siren, Claiming Adequacy(sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulphur, chlorine, argon)
Period 3-4:
(Elements 19-27):Kindly Cannibals Scare Timid Visitors, Cruelly Menacing Feeble Communist(potassium, calcium, scandium, titanium, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt)

Hydrogen Helium Periodic Table
twits Cuddling Zany Ga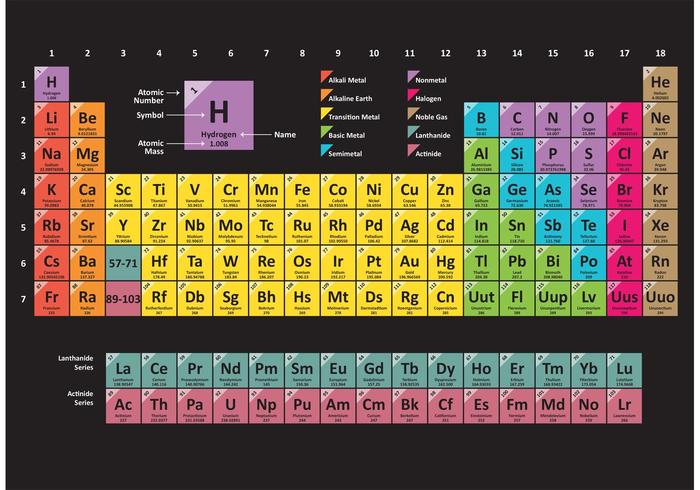 bbling Geese
bbling Geese Hydrogen Helium Lithium Table
AstrideHydrogen Vs Helium
SeHelium Vs Hydrogen Balloon
veral British Kangaroos(nickel, copper, zinc, gallium, germanium, arsenic, selenium, bromine, krypton)All matter consists of atoms of one or another element such as hydrogen (H) or oxygen (O), often combined into compounds (as in H2O=water). The elements are set in a Periodic Table in the order of their atomic weights (starting with hydrogen, the lightest) following Mendeleev's Periodic Law, which states that 'the properties of the elements are in periodic dependence upon their atomic weights' - in other words, elements either eight or ten places apart have many properties in common. See rare earths for the order of rare earth elements and rare gases for a mnemonic sentence governing the order of rare gases. For those completely unfamiliar with the Periodic Table itself, it is reproduced below in full.
