Mass Number Of Sulphur
- Sulfur (S - Standard atomic weight), molar mass. Sulfur or sulphur is a chemical element with symbol S and atomic number 16. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow crystalline solid at room temperature. Chemically, sulfur combines with all elements except for gold, platinum, iridium, nitrogen, tellurium, iodine and the noble gases.
- Uses of Sulfur - Sulphur is a chemical element with symbol S and atomic number 16. Know the Uses of Sulphur, Chemical Properties of Sulphur, Atomic Mass, Melting Point and more at BYJU'S.
From the question. Molar mass (M) of Sulphur = 32g/mol. N ( Sulphur) = 56/32 = 1.75mol. Since the moles of oxygen and sulphur are the same. M (O2) = 16 × 2 = 32g/mol. Mass of oxygen = molar mass × moles.
CHEBI:37983 - sulfur-35 atom
| Main | ChEBI Ontology | Automatic Xrefs | Reactions | Pathways | Models |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sulfur has a history that dates to ancient times. It was discovered around 2000 BCE by Chinese. Sulfur has diverse biological significance and have numerous industrial implications.
History and Discovery
Sulfur has been known since prehistoric times and has been used in ancient Greece, Egypt, China and India. In very early times, sulfur was named Torah, and was also mentioned in Bible, by the termed “brimstone”, which means “burning sulfur”. Sulfur was known for its bactericidal activity in Egypt and Greece and was used for fumigation and in medicines and ointments [1]. In China, as early as the 6th century BC, sulfur was known as shiliuhuang and was extracted from pyrite. It was used mainly in black gunpowder by the Chinese. Antoine Lavoisier, in 1777 propose that sulfurs is a distinct element and elemental sulfur was discovered in 1867.
Sulfur
| Periodic Table Classification | Group 16 Period 3 |
|---|---|
| State at 20C | Solid |
| Color | Yellow |
| Electron Configuration | [Ne] 3s2 3p4 |
| Electron Number | 16 |
| Proton Number | 16 |
| Electron Shell | 2, 8, 6 |
| Density | 2,07 g.cm-3 at 20°C |
| Atomic number | 16 |
| Atomic Mass | 32,06 g.mol -1 |
| Electronegativity according to Pauling | 2.58 |
Occurrence
Sulfur is quite abundant on Earth as well as in the universe. Its ranked 10th in order of abundance among all elements in the universe. Sulfur is created in huge stars and is present in various kinds of meteorites. It is produced during fusion reaction between nucleus of helium and silicon. In the Earth’s crust, sulfur is the 5th most abundant element by mass. It is ubiquitous in volcanic regions and in hot soring areas of the world. The Pacific Ring of Fire is especially known for its abundance in sulfur reserves. Sulfur is also found in native form on earth and is formed because of metabolic activity of anerobic bacteria that degrade sulfate minerals. The most common mineral of sulfur includes, gypsum, pyrite, barite, cinnabar and galena. Sulfur is also released into environment, especially in tropical areas, by the weathering of mineral ores. Currently, sulfur is produced from natural gas, petroleum and fossil reserves. The largest producers of sulfur include China, Canada Japan, Chile and Indonesia. Sulfur is a vital component of all living cells and is embedded in the proteins, DNA, and large variety of enzymes of plants, animals and microbes. Human body is comprised of various forms and compounds of sulfur and is considered as the eight most abundant element by weight in the human body.
Physical Characteristics
Sulfur is a yellow color crystalline non-metal that is solid at room temperature. Sulfur exists in various allotropic forms and have around 30 solid allotropes. It has the highest number of allotropes among all elements. Octasulfur, cycle-S8 is the most common allotrope of sulfur [2]. Sulfur is insoluble in water.
Chemical Characteristics
Sulfur is a reactive metal. It forms compounds with all other elements, except nitrogen, gold, iodine, platinum and the Nobel gases. Upon combustion, sulfur gives out a blue flame and produces sulfur oxide that has pungent odor. Sulfur have various oxidation states, +2, +4 ,+6 and +6 and +4 are more common [3].
Significance and Uses
- Sulfur is widely used to make fertilizers, such as calcium sulfate.
- Sulfur is used in various agrochemicals, such as fungicides and insecticides. Dusting of elemental sulfurs in powdered form has been used widely to eliminate the growth of fungus from grapes, and many vegetables. It is also used as insecticide to eliminate ticks and mites from crops and plants.
- Various compounds of sulfur, especially organo-sulfurs are wieldy used in pharmaceutical industry. A large group of drugs, termed as sulfa drugs are broad spectrum antibacterial sulfonamides. Similarly, penicillin and cephalosporin contain sulfur.
- Sulfurs is widely used for fumigation purposes.
Health Hazards
Sulfur is non-toxic. However, burning of sulfur can lead to production of sulfur dioxide gas, which at high concentration can lead to damaging effects on eyes, lungs and other tissues. Similarly, other compounds of sulfur, including sulfuric acid is highly corrosive acid and its fumes are damaging to the eyes and nasal linings. Hydrogen sulfide is a highly toxic compounds and resembles cyanide in its toxicity.
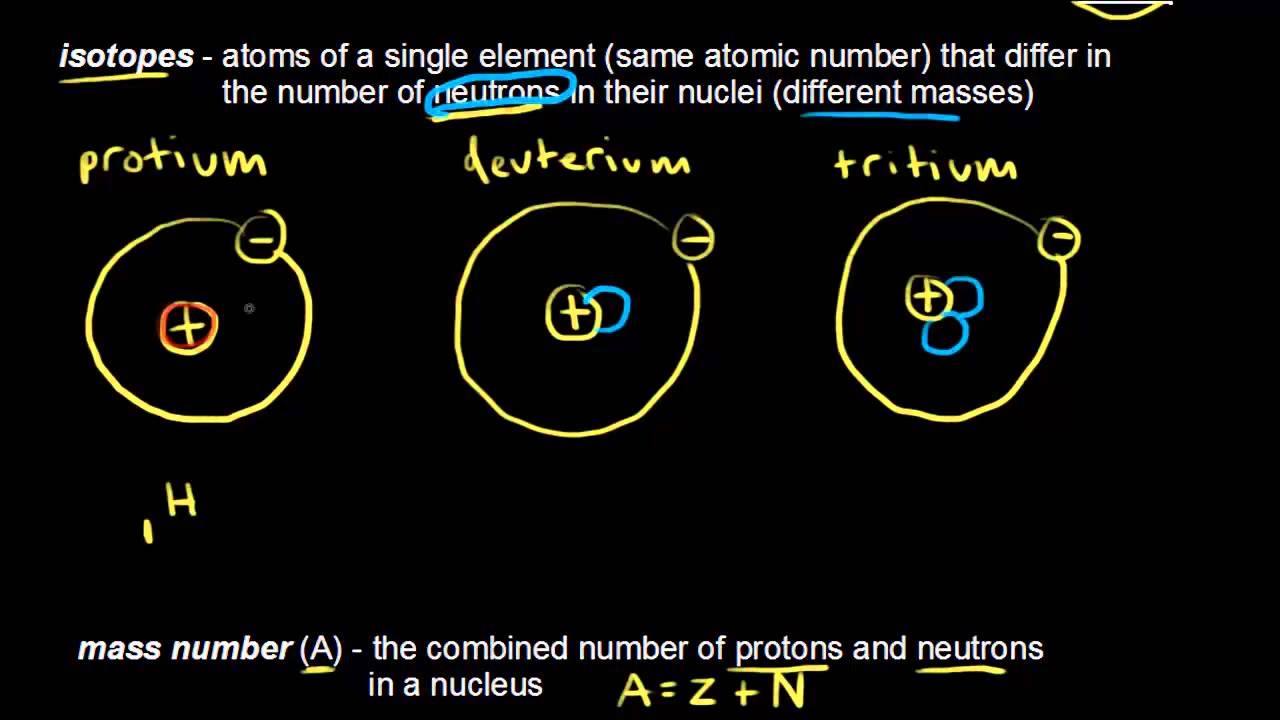
Isotopes of Sulfur
There are 25 natural isotopes of sulfur and only four are stable, including sulfur-32, sulfur-33, sulfur-34, and sulfur-36 [4]. There are also various radioactive isotopes of sulfur, among which only sulfur-35 have a relatively ling half-life (85 days) and all others are significantly unstable.
REFERENCES
Synology for mac. [1]. Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN0-7506-3365-4.
[2]. Steudel, Ralf; Eckert, Bodo (2003). Solid Sulfur Allotropes Sulfur Allotropes. Topics in Current Chemistry. 230. pp. 1–80. doi:10.1007/b12110. ISBN978-3-540-40191-9.
Mass Number Of Sulphur 32

[3]. Egon Wiberg; Nils Wiberg (2001). Inorganic Chemistry. Academic Press. pp. 513–. ISBN978-0-12-352651-9.
Mass Number Of Sulfur -2
[4]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-planetary-sciences/sulfur-isotopes
Atomic Mass No Of Sulphur
Other Periodic Table Elements
- Beryllium
Beryllium is an ancient element and is characterized as an alkaline earth metal. It is…
- Manganese
Manganese is an ancient metal and was discovered as a distinct element in 1774. Azure file storage explorer download. It…
- Tantalum
Tantalum was discovered in in 1802 by Anders Ekeberg. It is resistant to corrosion and…

